Underrated Ideas Of Info About Why Is PCB Damaged

Understanding PCB Damage
1. What Exactly are PCBs Anyway?
Printed Circuit Boards, or PCBs, are basically the unsung heroes of modern electronics. Think of them as the nervous system of your smartphone, laptop, or even your car. They're the green (or sometimes other colors!) boards with all those intricate lines and components that connect everything and allow electricity to flow where it needs to go. Without them, your favorite gadgets would be just fancy paperweights.
These boards aren't invincible, though. They can get damaged, leading to all sorts of electronic mayhem. Identifying why a PCB is damaged is crucial for preventing future issues and maybe even rescuing that seemingly dead device. It's like being a detective, but instead of solving a crime, you're solving an electronic puzzle. And trust me, the reward of reviving a beloved gadget is pretty satisfying.
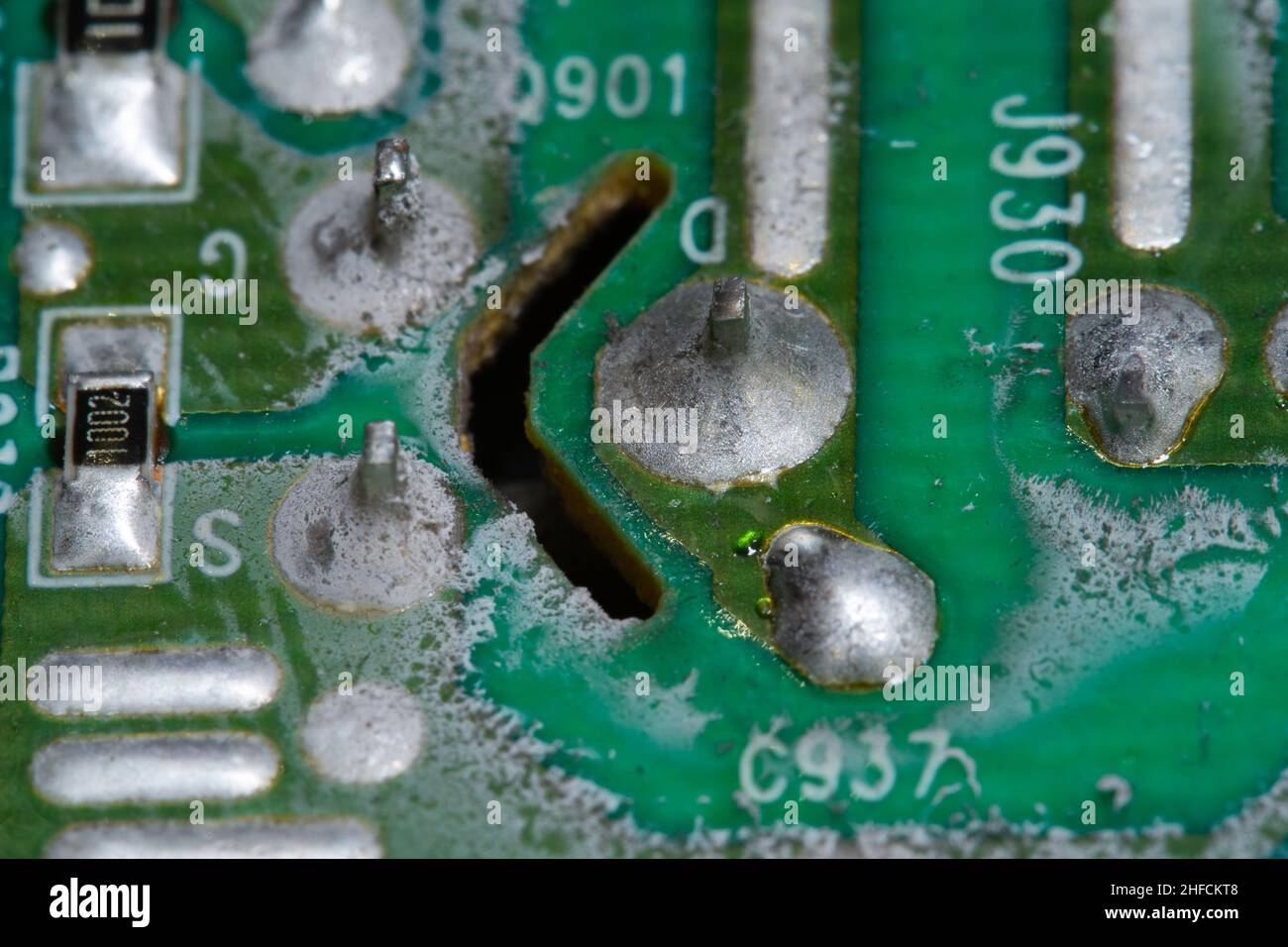
So, what kind of damage are we talking about? Well, it ranges from the obvious — like a charred spot from a short circuit — to the less visible, such as hairline cracks or corrosion. Each type of damage has its own cause, and understanding these causes is the key to keeping your PCBs healthy.
Think of it this way: a healthy PCB is a happy PCB, and a happy PCB means a happy user (that's you!). Let's dive into the common culprits behind PCB damage and how to avoid them. Because nobody wants a paperweight, right?
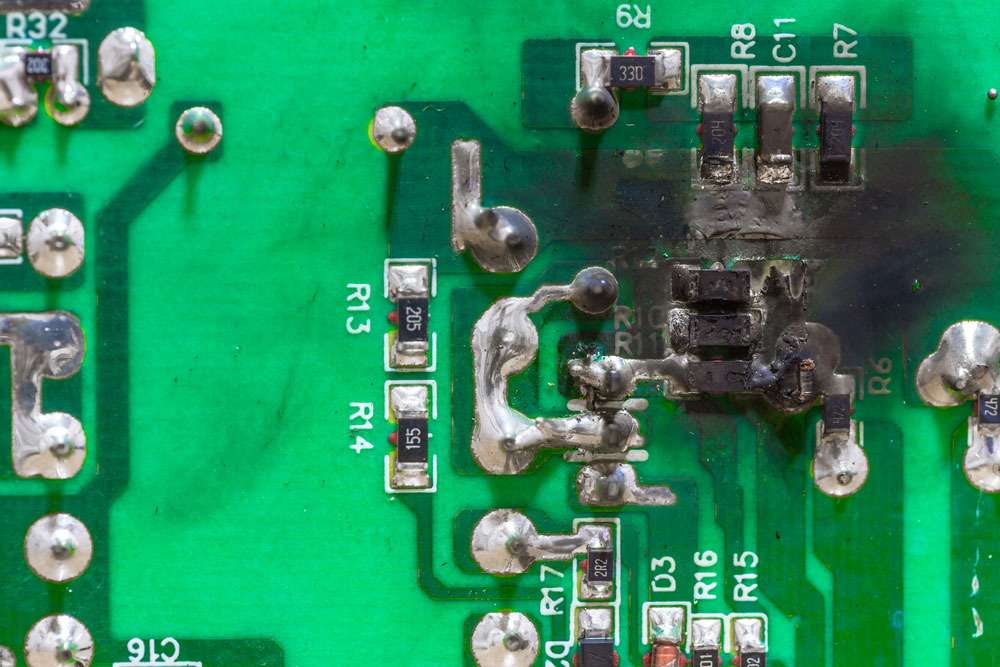
Short Circuit Board PCB Damage Caused By Current Diversion/Low Resistance
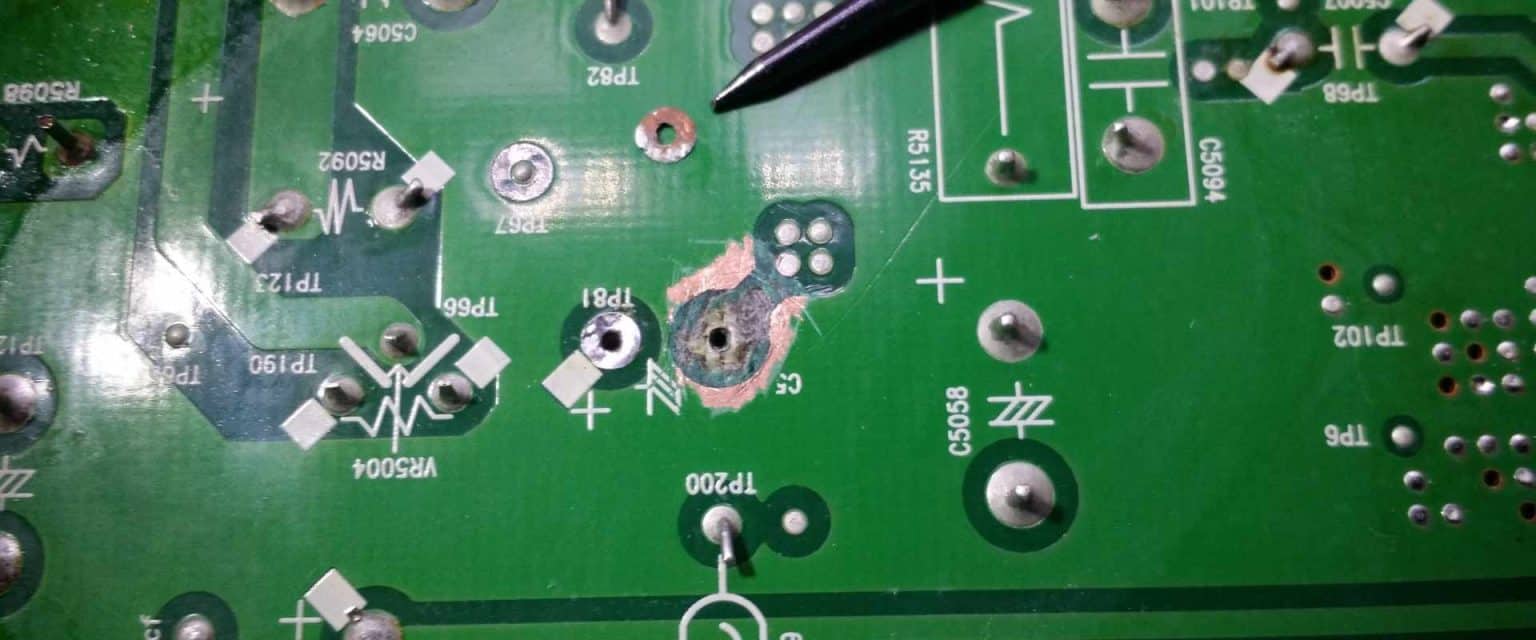
Common Culprits Behind PCB Problems
2. Heat
Excessive heat is a major enemy of PCBs. Just like leaving your chocolate in the sun, subjecting a PCB to high temperatures can cause serious problems. Components can overheat, solder joints can melt, and the board itself can warp or even delaminate (that's when the layers of the board start to separate). Not good!
Where does this heat come from? Often, it's from the components themselves. Powerful processors or poorly heatsinked components can generate a lot of heat. Poor ventilation is another factor; if the heat can't escape, it just builds up. It's like being stuck in a crowded elevator on a hot day — everyone's uncomfortable.
To prevent heat damage, make sure your electronic devices have adequate ventilation. Consider using heat sinks and fans to dissipate heat. And avoid leaving your devices in direct sunlight or in hot environments. Think of your PCB as a delicate flower; it needs to be kept cool and comfortable.
Also, be mindful of the operating temperatures of the components on your PCB. Exceeding their rated limits is a surefire way to shorten their lifespan and potentially damage the board. Reading datasheets might sound boring, but it's a small price to pay for avoiding a costly repair.
3. Moisture
Water and electronics generally don't mix. Moisture can lead to corrosion, which weakens solder joints, degrades components, and can even cause short circuits. It's like rust on a car — it slowly eats away at the metal until it's compromised.
The problem isn't always obvious. Sometimes, it's just humidity in the air that causes the damage over time. Other times, it's a direct spill or exposure to rain. And even if the water dries, the residue can still cause corrosion.
Protecting your PCBs from moisture is crucial. Conformal coatings are a great way to create a barrier against moisture and other contaminants. These coatings are thin, protective layers that are applied to the board after assembly. They're like a raincoat for your PCB.
If your device does get wet, don't panic! Immediately disconnect the power source and allow it to dry thoroughly before attempting to use it again. Using a desiccant like silica gel can help speed up the drying process. And resist the urge to turn it on to "see if it still works." That's a recipe for disaster!
4. Physical Stress
PCBs, while sturdy in some respects, are also brittle. Bending, twisting, or dropping a device can cause cracks in the board, which can break circuits and lead to all sorts of problems. It's like a dry twig; it snaps easily under pressure.
This is especially common in portable devices like smartphones and laptops, which are often subjected to a lot of handling. Even something as simple as inserting or removing a connector too forcefully can put stress on the board.
To minimize physical stress, handle your devices with care. Avoid dropping them or putting them under excessive pressure. When inserting or removing connectors, be gentle and use the correct tools. And consider using a protective case or enclosure to provide extra support.
Also, pay attention to the design of the PCB itself. Proper mounting and support can help to distribute stress and prevent cracks. It's like building a house; a solid foundation is essential for stability.
5. Electrical Overstress
Just like humans, PCBs can be overwhelmed by too much electricity. Voltage spikes, surges, or electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage components and cause the board to fail. It's like trying to power your entire house with a single AA battery; it just won't work.
Voltage spikes can come from various sources, such as lightning strikes, power grid fluctuations, or even faulty equipment. ESD can occur when you touch a sensitive electronic component after walking across a carpet on a dry day. That little zap you feel can be devastating to a PCB.
To protect your PCBs from electrical overstress, use surge protectors and power conditioners to filter out voltage spikes. Ground yourself before handling sensitive electronic components to prevent ESD. And be careful when working with high-voltage circuits.
Also, consider using components that are rated for higher voltages and currents than what is normally required. This provides a safety margin and helps to prevent damage from unexpected surges. It's like buying a car with extra airbags; you hope you never need them, but they're there if something goes wrong.

Diagnosing PCB Damage
6. Visual Inspection
The first step in diagnosing PCB damage is a thorough visual inspection. Look for any signs of discoloration, burning, cracks, corrosion, or broken components. A magnifying glass can be helpful for spotting small details.
Pay particular attention to the areas around connectors, components that generate a lot of heat, and any areas that have been exposed to moisture. These are the most likely places to find damage.
If you see any signs of damage, don't attempt to power on the device. This could make the problem worse and potentially cause further damage. Instead, take detailed photos of the damage for documentation purposes.
Visual inspection is like being a doctor; you look for the obvious symptoms first before running more tests. It's not always conclusive, but it can often point you in the right direction.
7. Testing with a Multimeter
A multimeter is an essential tool for diagnosing electrical problems on PCBs. It can be used to measure voltage, current, and resistance, which can help you identify short circuits, open circuits, and other electrical faults.
Before using a multimeter, make sure you understand how to use it safely and correctly. Incorrect measurements can damage the multimeter or even the PCB. There are plenty of tutorials and guides available online.
Start by checking the power supply voltages to make sure they are within the correct range. Then, check the continuity of critical circuits to identify any breaks in the wiring. And finally, measure the resistance of components to see if they are within their specified values.
Using a multimeter is like being an electrician; you use your knowledge of electricity to track down faults and diagnose problems. It requires patience and attention to detail, but it can be very rewarding when you finally find the culprit.
8. Smell Test
Okay, this might sound a bit strange, but sometimes the smell can tell you a lot about a damaged PCB. A burning smell is a classic sign of overheating or a short circuit. A fishy smell can indicate capacitor failure. And a musty smell can indicate moisture damage.
Of course, the smell test is not a definitive diagnosis. But it can be a useful clue, especially when combined with visual inspection and multimeter testing. It's like being a detective; you use all your senses to gather evidence.
But please, don't go around sniffing every PCB you see. Some components can release harmful fumes when they are damaged. So be careful and use common sense.
In summary, smelling isn't the main method to identify damaged PCB, but it is better than nothing when you had nothing.
The Common Causes Of PCB Failure Global Electronic Services
Preventing PCB Damage
9. Proper Handling and Storage
Handle PCBs with care and store them in a dry, clean environment. Avoid dropping them, bending them, or exposing them to excessive heat or moisture. It's like handling a delicate piece of art; you want to protect it from damage.
Use antistatic bags and wrist straps when handling sensitive electronic components to prevent ESD damage. And avoid touching the conductive traces or components on the board with your bare hands.
When storing PCBs, keep them in a sealed container with a desiccant to absorb any moisture. And avoid storing them in direct sunlight or in hot environments.
By taking these simple precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of PCB damage and extend the lifespan of your electronic devices. It's like preventative maintenance on your car; it's worth the effort in the long run.
10. Thermal Management
Implement effective thermal management strategies to prevent overheating. Use heat sinks, fans, and thermal interface materials to dissipate heat away from components that generate a lot of heat. It's like installing air conditioning in your house; it keeps everything cool and comfortable.
Make sure your devices have adequate ventilation to allow heat to escape. And avoid blocking the vents or placing your devices in enclosed spaces.
Monitor the temperature of your components to ensure they are operating within their specified limits. And adjust your thermal management strategies as needed to keep them cool.
Proper thermal management is essential for preventing PCB damage and ensuring the reliable operation of your electronic devices. It's like taking care of your engine; it keeps everything running smoothly.
11. Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Regularly inspect your PCBs for any signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or broken components. And perform routine maintenance, such as cleaning the board and replacing any worn or damaged components. It's like getting a regular checkup at the doctor; it helps to catch problems early before they become serious.
Clean the board with a soft brush and isopropyl alcohol to remove any dust or debris. And use a contact cleaner to clean any dirty or corroded connectors.
By catching problems early and performing routine maintenance, you can prevent PCB damage and extend the lifespan of your electronic devices. It's like taking care of your teeth; it prevents cavities and other dental problems.
FAQ
12. Q
A: It depends on the extent of the damage. Minor damage, such as a broken trace or a loose component, can often be repaired. However, severe damage, such as a cracked board or extensive corrosion, may be irreparable. It's always worth consulting with a qualified electronics technician to assess the damage and determine if repair is possible. But sometimes, the damage is simply too much, and it's time to say goodbye.
13. Q
A: The cost of repairing a damaged PCB can vary widely depending on the type and extent of the damage, as well as the complexity of the board. Simple repairs, such as replacing a capacitor, may cost only a few dollars. But more complex repairs, such as replacing a microchip or repairing a cracked board, can cost hundreds of dollars. It's best to get a quote from a qualified electronics technician before proceeding with any repairs. Sometimes it is cheaper to buy a new one!
14. Q
A: The signs of a failing PCB can vary depending on the type of device and the nature of the damage. Common signs include erratic behavior, intermittent failures, overheating, unusual smells, and visual damage. If you notice any of these signs, it's important to investigate the issue promptly to prevent further damage. Delaying investigation might lead to irreversible damage. It's better to be safe than sorry!
15. Q
A: It depends on the nature of the damage. If the board is visibly damaged or if there is a burning smell, it's best to avoid handling it directly. Some components can release harmful fumes when they are damaged. If you must handle the board, wear gloves and eye protection to protect yourself from potential hazards. Also, it's crucial to disconnect the power source before handling any electronic device.
