Great Info About Is Electric Car AC Or DC
Energies Free FullText A Review Of DCAC Converters For Electric
Electric Cars
1. Understanding the Basics of Electricity
Okay, so you're thinking about joining the electric car revolution, fantastic! But then you start hearing about AC and DC, and suddenly it feels like you're back in high school physics, right? Don't worry, it's not as scary as it sounds. Think of it like this: electricity comes in two main flavors, Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). AC is like a wave, going back and forth, while DC is like a steady stream, flowing in one direction. Think of a river versus the ocean's tide.
Your house runs mostly on AC. That's what comes out of your wall sockets and powers your TV, your refrigerator, and your questionable collection of 80's memorabilia. DC, on the other hand, is what batteries use — like the one in your phone or, crucially, the one in your electric car! Now, where things get interesting is how these two currents interact within your EV. Its a bit like a complicated dance, with converters and inverters shuffling things around behind the scenes.
The battery in your electric car stores energy as DC. This is important! It's fundamental to how EVs work. But here's the kicker: sometimes you'll charge your car using AC power (like from a standard wall outlet). So, what gives? Well, that's where the onboard charger comes in. It acts like a translator, converting the AC power from the grid into DC power that your battery can actually use and store. Think of it as a tiny electrical interpreter living inside your car.
This conversion process isn't perfectly efficient, by the way. Some energy is always lost in the translation, which is why charging at home with a standard outlet often takes longer than using a DC fast charger. And that's what makes the charging process, let's say, a little bit more complicated. Now, before you run screaming back to gasoline, stick with me. It gets better!

How Does Air Conditioning Work In An Electric Vehicle?
The Role of AC and DC in Charging
2. Home vs. Fast Charging
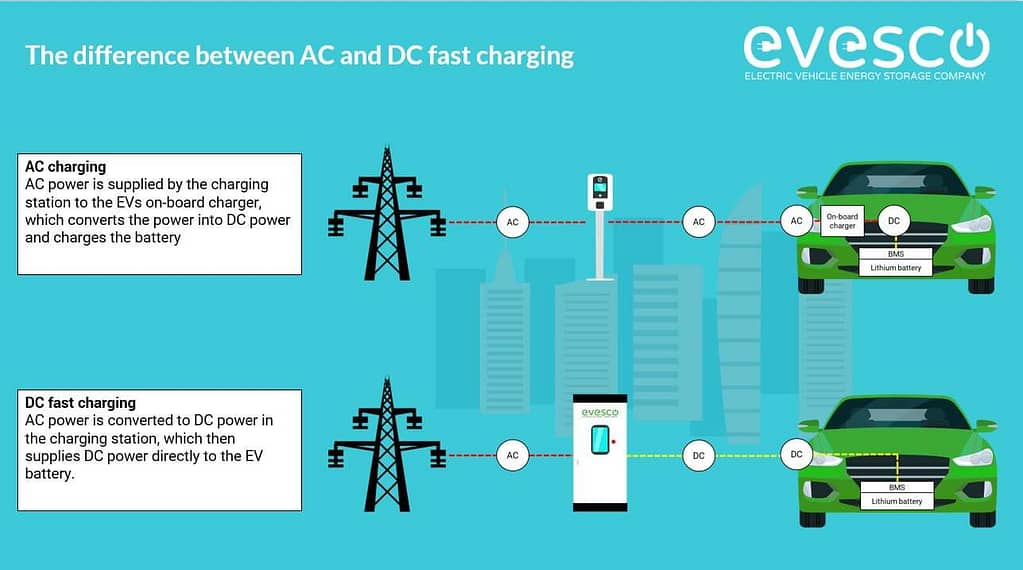
So, we've established that your electric car's battery wants DC. But most of the electricity coming into your home is AC. That means if you're charging at home (Level 1 or Level 2 charging), your car's onboard charger is doing the AC-to-DC conversion. This is generally a slower process, but it's convenient for overnight charging or topping off your battery while you're, say, binge-watching that show everyone's talking about.
Now, enter the DC fast charger! These chargers, often found at public charging stations, are like superheroes of the electric car world. They bypass your car's onboard charger altogether and deliver DC power directly to the battery. This is why they can charge your car much faster — sometimes in as little as 30 minutes. The charging station itself handles the AC-to-DC conversion, delivering the good stuff directly to your car's battery. Think of it as a direct injection of energy!
The speed difference between AC and DC charging is significant. Imagine filling a bathtub with a garden hose versus a fire hose. That's essentially the difference. Level 1 charging (standard wall outlet) is like a dripping faucet, Level 2 charging (240V outlet) is like a garden hose, and DC fast charging is the aforementioned fire hose. You can see why DC fast charging is the preferred method when you're on a road trip and need a quick jolt of energy.
The type of charging also influences the components inside your electric car. The onboard charger is a critical component, but it's not needed when DC fast charging, leaving you with less to worry about and more time to enjoy your electric vehicle! Keep in mind that not all electric cars are created equal. Some cars can handle higher DC charging rates than others, so check your car's specifications to get the most out of your charging experience.
The Different Levels Of EV Charging Explained EVESCO
Inside the Electric Car
3. The Onboard Charger and Inverter
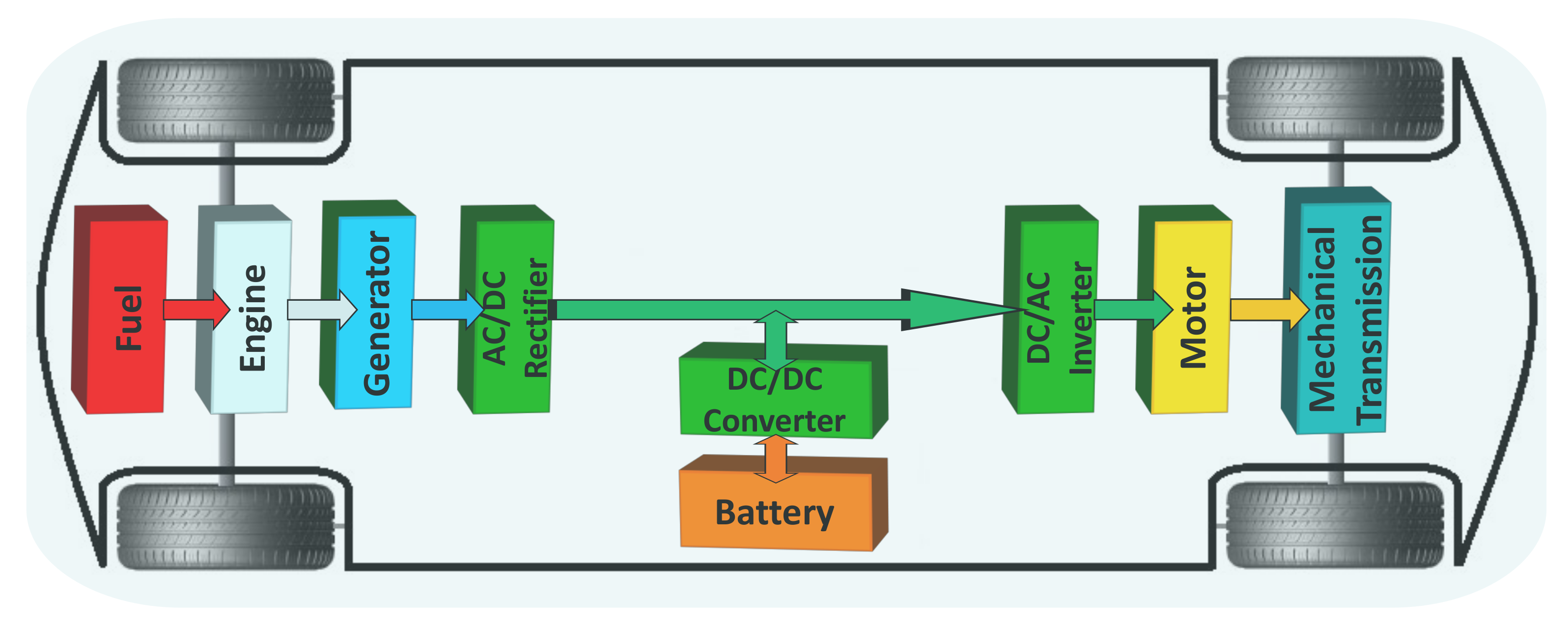
Let's take a peek under the hood (or wherever the electrical components are located in your particular EV). Inside, you'll find a few key players responsible for managing the flow of electricity. First, there's the onboard charger, which we've already discussed. It converts AC power from the grid into DC power for the battery when you're charging using a standard outlet or a Level 2 charger.
But wait, there's more! Electric motors, the things that actually turn the wheels and make your car move, often run on AC power. So, your car also needs an inverter! An inverter does the opposite of the charger; it converts the DC power from the battery back into AC power for the motor. It's like a reverse translator, making sure everything speaks the right language.
These components work together in a carefully orchestrated dance. When you accelerate, the battery sends DC power to the inverter, which converts it to AC to power the motor. When you brake (using regenerative braking), the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electricity, which is then converted back to DC and stored in the battery. It's a closed-loop system, designed to maximize efficiency and extend your driving range. Pretty clever, huh?
The efficiency of these conversions is crucial for the overall performance of your electric car. Higher efficiency means less energy is wasted as heat, allowing you to drive further on a single charge. Automakers are constantly working to improve the efficiency of onboard chargers, inverters, and motors to squeeze every last mile out of the battery. It's a continuous quest for electrical optimization!

12V/24V DC Car Truck Air Conditioning System Electric AC Compressor
Beyond the Basics
4. The Evolution of EV Batteries
The type of battery used in an electric car is another important piece of the puzzle. Most EVs use lithium-ion batteries, similar to those found in your smartphone or laptop, but on a much larger scale. These batteries store energy as DC, and their performance characteristics (like energy density, charging speed, and lifespan) significantly impact the overall driving experience.
Battery technology is constantly evolving. Researchers are working on new battery chemistries, like solid-state batteries, which promise higher energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety. These advancements could revolutionize the electric car industry, making EVs even more attractive to consumers. Imagine a future where you can charge your car in just a few minutes and drive hundreds of miles on a single charge!
The management of the battery — the Battery Management System (BMS) — is also crucial. The BMS monitors the battery's temperature, voltage, and current, ensuring that it operates within safe limits and maximizes its lifespan. It also plays a role in balancing the charge across individual battery cells, preventing any one cell from becoming overcharged or over-discharged. It's like a vigilant guardian, protecting the battery from harm.
The future of electric car batteries is bright. With ongoing research and development, we can expect to see even more improvements in battery technology in the years to come. This will lead to longer driving ranges, faster charging times, and lower costs, making electric cars an even more compelling alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. Get ready for the electric revolution!

Real-World Implications and Considerations
5. Choosing the Right Charging Solution
So, now that you have a better understanding of AC and DC in electric cars, how does this knowledge translate into the real world? Well, it affects your charging choices. If you mostly drive short distances and have access to overnight charging at home, a Level 2 charger might be all you need. It's a convenient and cost-effective solution for daily commuting.
However, if you frequently take long road trips, you'll want to rely on DC fast charging stations. These stations can significantly reduce your charging time, allowing you to get back on the road quickly. Keep in mind that DC fast charging is typically more expensive than charging at home, so factor that into your travel budget.
The availability of charging infrastructure is also a crucial consideration. Before embarking on a long journey, plan your route and identify charging stations along the way. There are numerous apps and websites that can help you locate charging stations and check their availability. A little bit of planning can go a long way in avoiding range anxiety and ensuring a smooth and enjoyable road trip.
And finally, consider the long-term impact of your charging habits on your battery's lifespan. Frequent DC fast charging can potentially degrade the battery faster than slower AC charging. However, automakers are constantly improving battery technology and management systems to mitigate this effect. Consult your car's manual for recommendations on the best charging practices to maximize the lifespan of your battery.
Download EV Charging Modes Of Electric Car Explained. AC Alternating
FAQs About AC and DC in Electric Cars
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Still have questions swirling around in your head? Don't worry, you're not alone. Here are some frequently asked questions about AC and DC in electric cars:
Q: Can I use a regular wall outlet to charge my electric car?
A: Yes, you can! This is called Level 1 charging. It's the slowest charging method, but it's convenient if you don't have access to a Level 2 charger. Just be prepared for a longer charging time.
Q: Is DC fast charging bad for my battery?
A: Frequent DC fast charging can potentially degrade the battery faster over the long term, but modern battery management systems are designed to minimize this effect. Consult your car's manual for recommendations on charging practices.
Q: What's the difference between Level 2 charging and DC fast charging?
A: Level 2 charging uses AC power that's converted to DC by your car's onboard charger. DC fast charging delivers DC power directly to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger, resulting in much faster charging times.
Q: Does temperature affect EV charging?
A: Yes! Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can impact charging speeds and battery performance. Batteries tend to perform best within a moderate temperature range.