Exemplary Info About Which Topology Is Best Why
Network Topology Star What Is With Exam Vrogue.co
Unraveling the Mystery
1. What even is a Network Topology?
Alright, let's dive into the world of network topologies. Basically, it's the blueprint of how devices are connected in a network. Think of it like the layout of streets in a city, or the way different rooms are arranged in a house. Each topology has its own unique way of connecting everything, and that affects how data flows, how reliable the network is, and even how much it costs to set up.
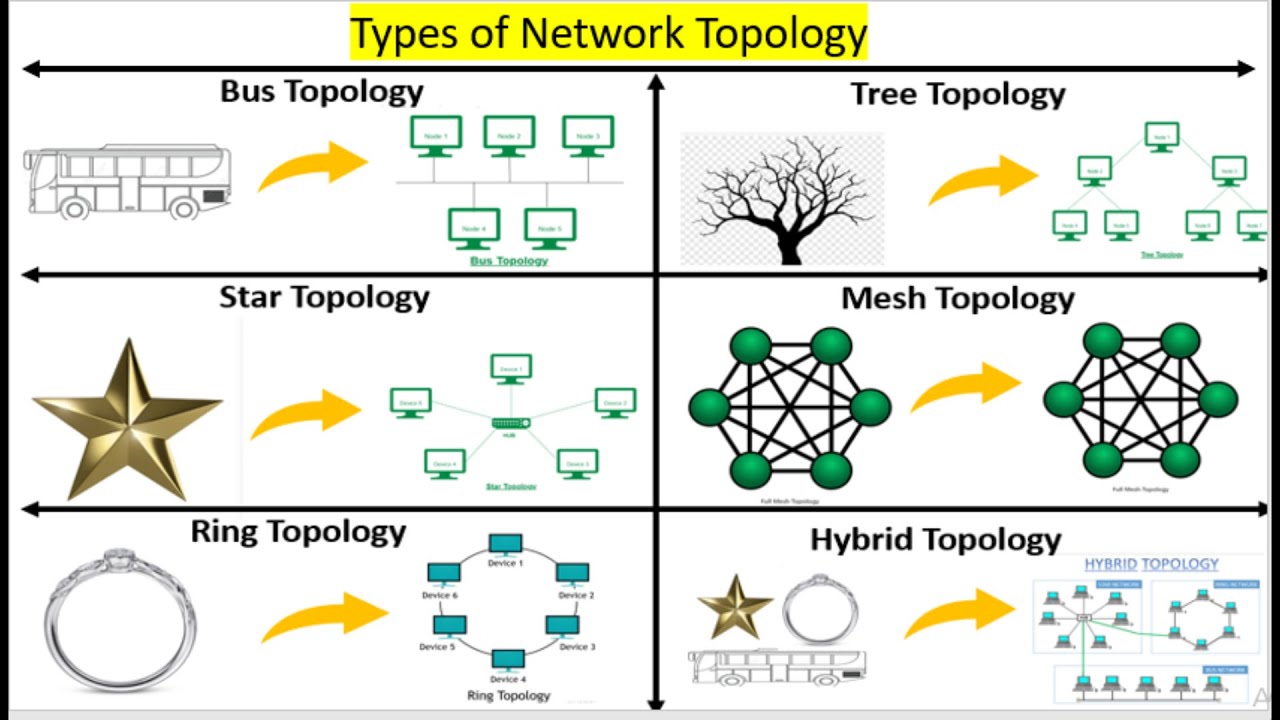
There are several common types like bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree, and each one has pros and cons. Choosing the right one depends on what you need from your network. Are you prioritizing speed? Redundancy? Cost-effectiveness? It's a bit like picking the right tool for the job a hammer won't do much good when you need a screwdriver.
You can think of it as choosing between a carefully planned garden and a wild, sprawling jungle. Both can be beautiful, but they require totally different approaches to maintain! Knowing the different topologies is key to building a network that actually works for you and does not lead you to a tech-headache later.
So, the question of which topology is best — (see what I did there? Keyword alert!) — it's a bit of a loaded one. It truly boils down to your specific needs. What works for a small office probably won't work for a large corporation, and what's perfect for a home network might be overkill for a tiny startup.
Types Of Network Topologies (Bus, Star, Ring, Tree, Mesh, Hybrid) Using
A Rogues' Gallery of Topologies
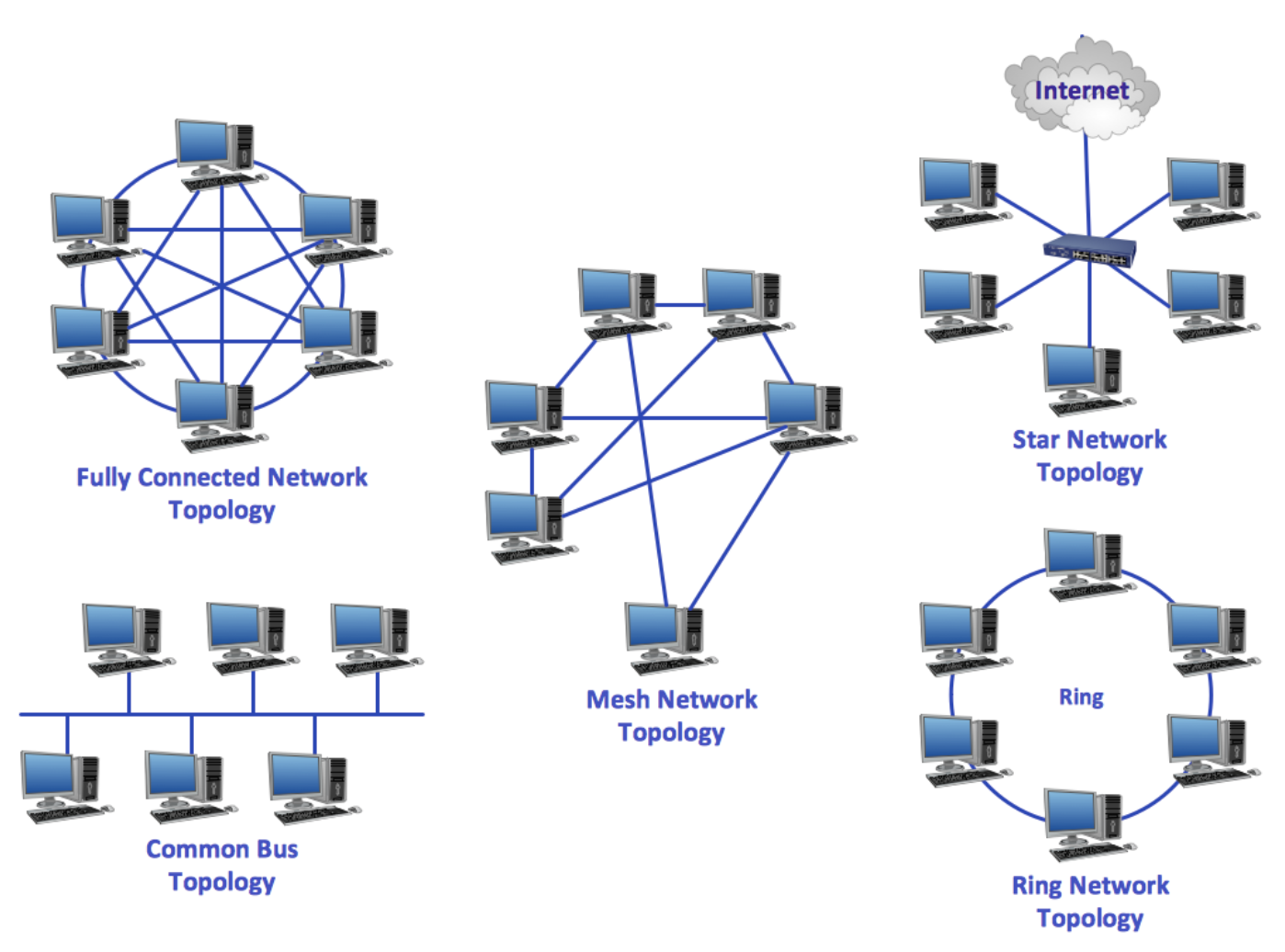
2. Bus Topology
Picture this: everyones connected to a single, long cable. Thats the bus topology. Its relatively easy to set up and doesn't cost a ton. Imagine stringing Christmas lights together in a straight line. If one bulb goes out, everything downstream stops working.
The main problem is if that central cable breaks, the entire network goes down. Its like cutting the main artery. Plus, as more devices are added, the network can slow down significantly, as everyone is sharing the same communication line. It can be a real bottleneck, especially with today's data-hungry applications.
Think of it like a one-lane highway at rush hour. Everyone's bumper-to-bumper, and you might even consider abandoning ship and walking. This topology is really less ideal these days because of those reasons. If your data needs were light, this would be perfect, but that isn't usually the case in today's world.
So, while simple and cheap, the bus topology is generally not recommended for anything beyond very small, non-critical networks. There are much better options for anything that requires reliability and speed, although you might still find them in some older legacy setups.
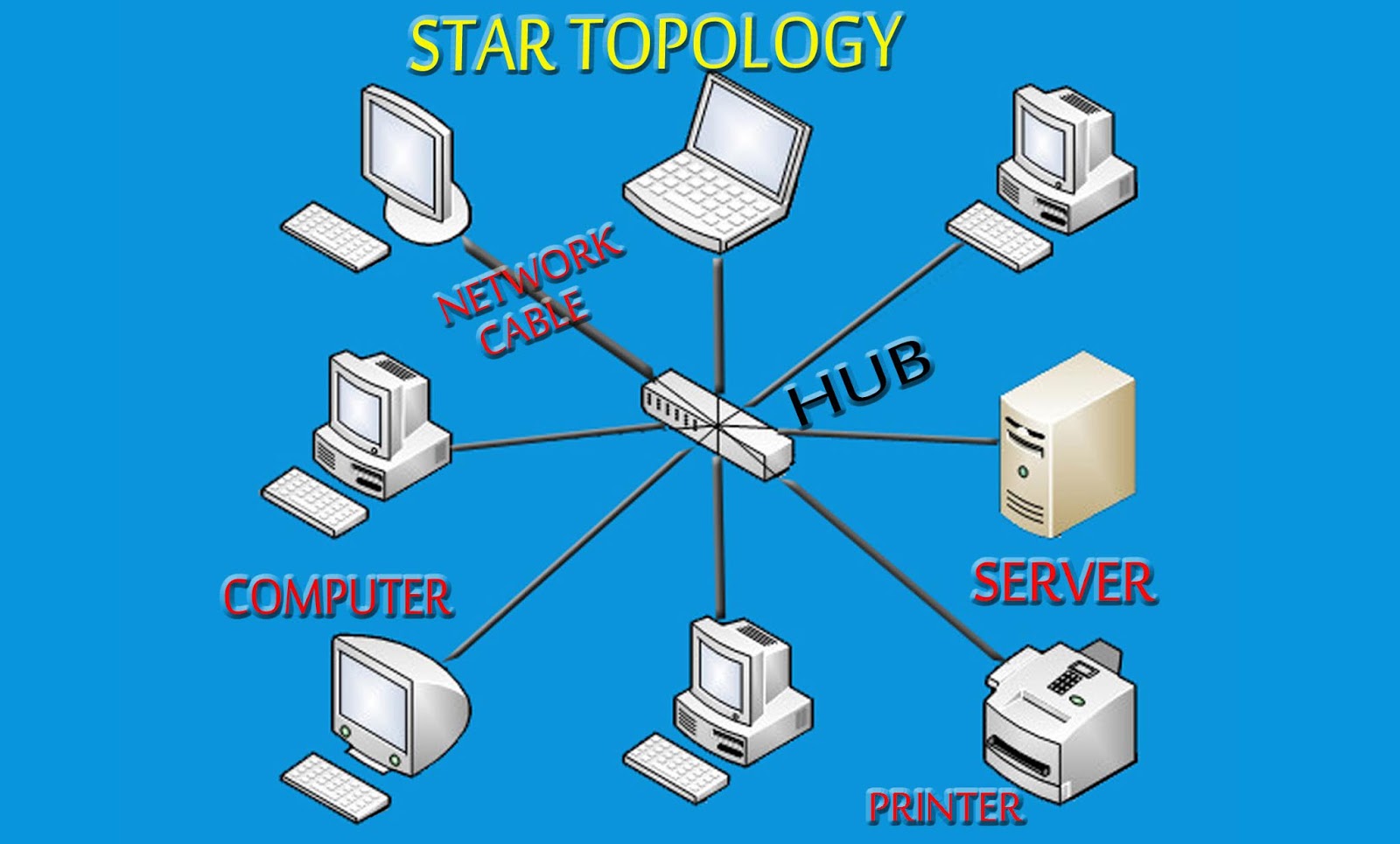
3. Star Topology
Now imagine a central hub or switch with each device connecting directly to it. Thats the star topology. It's much more robust than the bus topology. If one connection fails, only that device is affected. The rest of the network keeps humming along. This is one of the most common topologies in use today.
This is like having a city center where all the roads branch out individually. If one road is closed, the rest of the city can still function. However, if the central hub fails, everything goes down. So, that central hub is a critical point of failure — like the mayor having a bad day and shutting down the whole town.
The star topology is relatively easy to troubleshoot and manage. You can quickly isolate problems to specific connections. It's also easier to add or remove devices without disrupting the entire network. It's a good balance of cost, performance, and manageability.
While it's more expensive than a bus topology, the added reliability and manageability often make it worthwhile. Because the cable failure would only affect one device and not the whole system like with the bus, that is one of the reasons that makes the star topology so prevalent.
4. Ring Topology
In a ring topology, devices are connected in a closed loop. Data travels around the ring from one device to the next until it reaches its destination. Its like a relay race where each runner passes the baton (the data) to the next. This is a rarer topology and rarely used these days.
One major advantage is that data collisions are less likely because data only flows in one direction. Each device acts as a repeater, amplifying the signal as it travels around the ring. This helps to maintain signal strength over long distances.
However, if one device fails, it can break the entire ring. This is a major disadvantage. Also, adding or removing devices can be disruptive to the network. Think of it like trying to add a new runner to the middle of the relay race — its not going to be pretty!
Ring topologies are not as commonly used these days because of their vulnerability and complexity. They're often found in specialized applications where data collisions need to be minimized, such as some older token ring networks. Newer technologies offer the benefits of the ring but with the star topology.
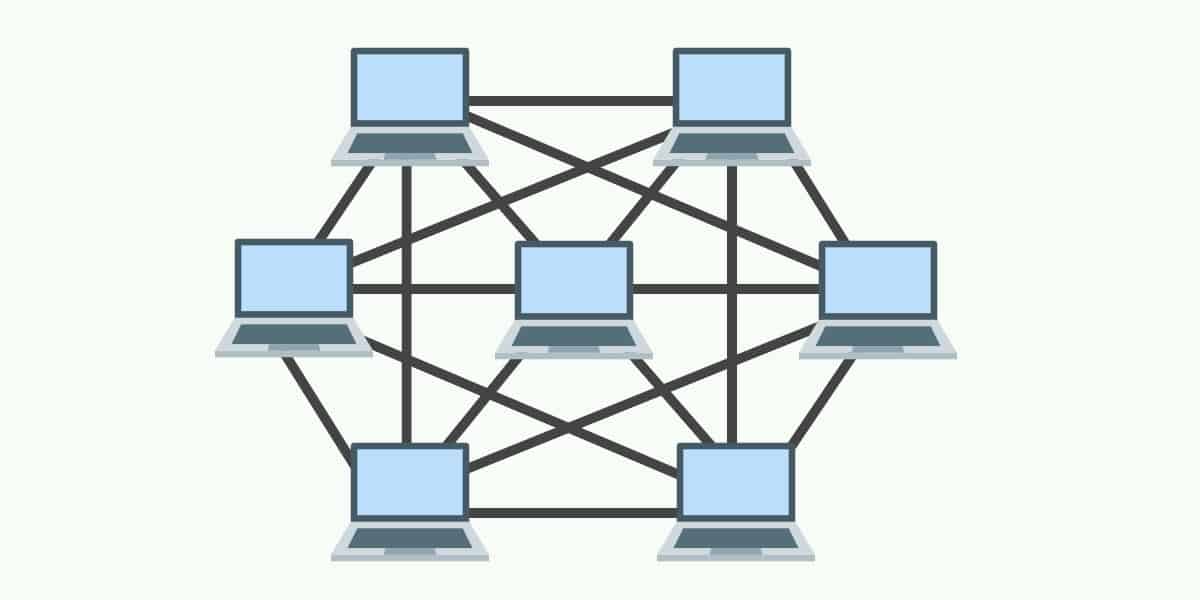
5. Mesh Topology
Now, for the mesh topology, picture every device connected to every other device. This is the most robust topology, but also the most expensive and complex. It offers multiple paths for data to travel, so if one connection fails, data can still reach its destination through another route.
This is like having multiple roads between every two points in a city. If one road is blocked, you can always take another route. The mesh topology is ideal for critical networks where downtime is unacceptable, like military or financial networks. But, with this also comes a heavy price tag.
The downside is the high cost of cabling and the complexity of managing all those connections. It's like trying to untangle a giant ball of yarn. Also, you will need an army of engineers with intricate knowledge of this specific topology.
Because the redundancy is so strong, the mesh topology is the most reliable choice. The cost and complexity often limit its use to specific applications where the benefits outweigh the drawbacks. If you need ultimate reliability and can handle the cost, mesh might be the way to go!
So, Which Topology Is Best? (The Truth!)
6. The Grand Finale
Alright, lets bring it all together. The "best" topology isnt a one-size-fits-all answer. It all depends on your specific needs, budget, and priorities. Consider the size of your network, the amount of traffic you expect, the level of reliability you need, and your budget. These are all important.
For a small home network or small business, a star topology is often a good choice. It's relatively easy to set up, manage, and is not too expensive. It's a good balance of performance and cost. Usually you can't go wrong with this one.
For larger organizations or critical applications, a mesh topology might be necessary to ensure high availability. You'll need to carefully weigh the cost and complexity against the benefits of redundancy.
Ultimately, choosing the right network topology is a balancing act. You need to weigh the pros and cons of each option and select the one that best meets your specific needs. Now the ball is in your court to decide which you will choose for your network.
Making Your Network Smarter
7. A Topology Is Only as Good as Its Implementation
Choosing a topology is just the beginning. A perfectly designed topology can still fail if not properly implemented and maintained. You'll need to consider things like cable quality, network hardware, and network management tools. Make sure your equipment is rated high!
Regularly monitor your network performance to identify potential problems before they cause downtime. Use network management tools to track traffic patterns, identify bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues. Think of it like giving your network a regular checkup to catch any potential problems early.
Plan for future growth and scalability. Choose a topology that can accommodate your evolving needs. You don't want to be stuck with a network that can't handle your growing business. It is important to make sure you plan accordingly and leave wiggle room for growth.
Stay up-to-date on the latest networking technologies and best practices. Networking is a constantly evolving field, so it's important to stay informed about new trends and technologies. The more knowledge you have, the better decision you can make for you company!

Assure1 RealTime Network Federation Enables Universal Topology & NOC
FAQ
8. Common Queries About Network Design
Okay, lets tackle some frequently asked questions about network topologies. Hopefully these will help clear up any lingering confusion.
Q: Can I combine different topologies in a single network?
A: Absolutely! This is called a hybrid topology. It is very common. For example, you might use a star topology for most of your network, but use a mesh topology for critical servers.
Q: What is the most secure network topology?
A: Security depends more on network configuration and security measures than on the topology itself. However, a mesh topology can provide some additional security by making it more difficult for attackers to compromise the entire network.
Q: How do I choose the right topology for my small business?
A: A star topology is usually a good starting point for small businesses. It's relatively easy to set up, manage, and is cost-effective. If you have specific needs, like high availability, you might consider a different topology or a hybrid approach.