Simple Info About What Is A Node And Junction
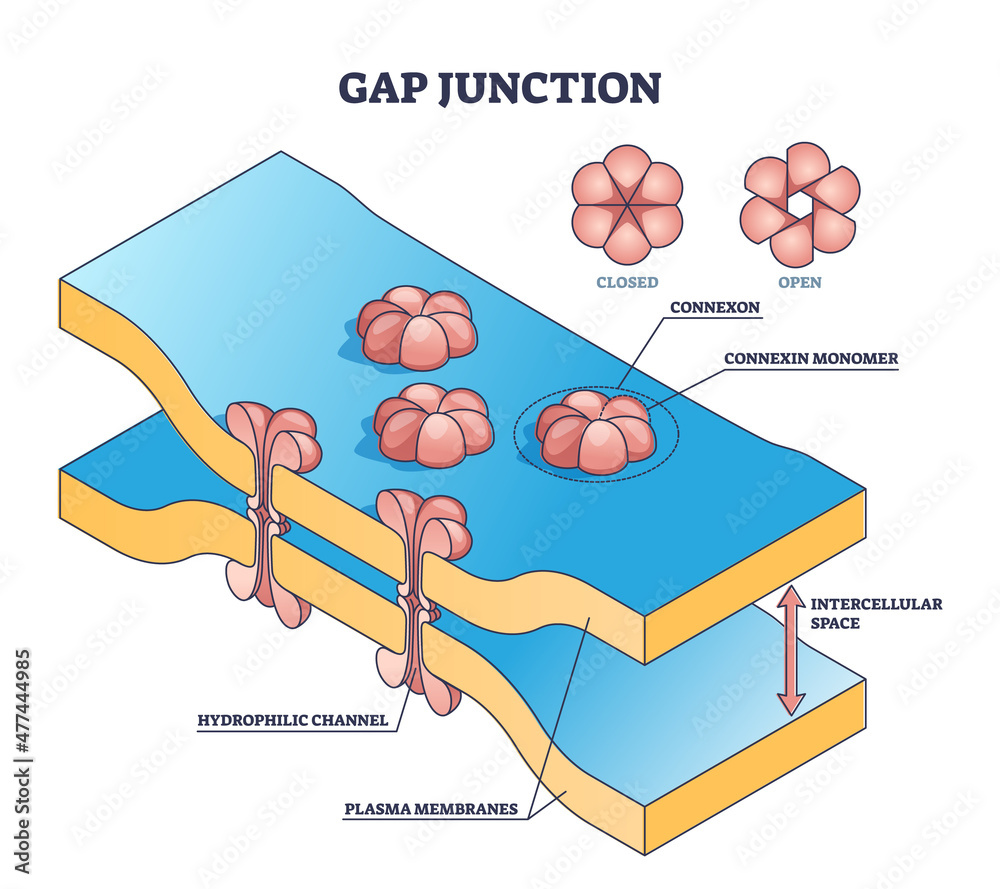
Understanding Nodes and Junctions
1. What exactly are nodes and junctions?
Ever found yourself staring at a complex diagram, maybe a network map or a circuit design, and feeling a bit lost in the sea of lines and shapes? Chances are, you've encountered nodes and junctions. These two terms are fundamental in various fields, from computer science to transportation planning. So, what are they, really? Let's break it down in a way that even your grandma could understand!
Imagine a road map. You've got all these roads connecting different cities and towns. Now, think of a city or town as a node. A node is essentially a point where things connect or intersect. It's a fundamental building block in any system involving relationships and connections. Think of it as the 'hub' in a network.
A junction, on the other hand, is specifically where two or more roads (or connections) meet. It's a type of node, but not all nodes are junctions. A lone town at the end of a dead-end road is a node, but not a junction. A bustling intersection where multiple roads converge? That's definitely a junction!
In essence, a node is a general term for a connecting point, while a junction is a specific type of node where multiple connections come together. Think of it like this: all squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares. All junctions are nodes, but not all nodes are junctions.
What Are Nodes And Links In Computer Network At Adeline Moore Blog
Delving Deeper
2. Nodes in Computer Science, Biology, and More!
The concept of a node isn't confined to just roads. It pops up in numerous fields, each with its own twist on the definition. Let's peek into a few:
Computer Science: In computer networks, a node can be a computer, a server, or any device connected to the network. Each node can send, receive, or forward information. It's like each house on your street being connected to the internet cable — each house is a node. And those Wi-Fi repeaters? Little node helpers, spreading the love.
Biology: Biology uses the node term to explain the part of a plant stem from which leaves or branches grow. A node could also be a lymph node, which plays a critical role in your immune system. These tiny bean-shaped structures are scattered throughout your body, acting as filters for harmful substances.
Transportation Networks: We already touched on this, but it's worth reiterating. Cities, intersections, airports — all nodes in a transportation network. They represent places where people and goods transfer or connect.Nodes in a field may have slightly different contexts, depending on which field it is being used. The underlying idea remains consistent — a node represents a key point of connection or activity within a system.

Intro To Circuits 15 What Is A Node? YouTube
Junctions
3. Exploring the Importance of Junctions
So, we know a junction is where multiple connections meet. But why is that important? Well, junctions are often the focal points for decision-making and resource allocation. Think about it:
Traffic Flow: A poorly designed road junction can lead to traffic congestion and accidents. Optimizing junction design is crucial for efficient traffic flow. Roundabouts, traffic lights, and even the subtle curvature of the road — all designed to make junctions safer and smoother.
Electrical Circuits: In electronics, junctions are where different components are connected. The design of these junctions is critical for the circuit's performance. Ever seen those tiny solder points on a circuit board? Those are junctions!
Decision Making: In a business context, a decision point where multiple departments or teams need to collaborate can also be considered a junction. Effective communication and coordination are essential for navigating these "junctions" successfully.Essentially, junctions are critical points that require careful planning and management to ensure things run smoothly. When things get too hectic at a busy intersection, problems arise! The same principle applies to any system with junctions, whether roads, circuits, or even complex processes within an organization.

Krayonnz Social Learning Network
The Relationship Between Nodes and Junctions
4. How Are They Different and How Are They Related?
It's easy to get nodes and junctions mixed up. Let's solidify their relationship with a simple analogy:
Imagine a social network like Facebook or X (formerly Twitter). Every individual profile is a node — a point in the network. Now, consider a group or community page. This is a junction where multiple individual nodes (profiles) come together and interact. Each individual person is a node, and then that person with other people is a junction.
Here's the key takeaway: junctions are always nodes, but nodes aren't always junctions. A node is simply a point of connection, while a junction is a specific type of node with multiple connections converging at that point.
Understanding this distinction can be helpful when analyzing complex systems. By identifying both nodes and junctions, you can gain a better understanding of how the system works and where potential bottlenecks or vulnerabilities might exist.
Think of it as building with LEGOs. You have individual blocks (nodes), and then you have those special connector pieces that link many blocks together (junctions). You need both to build something cool!

Branches, Nodes, & Loops With Series Parallel CircuitBread
Why This Matters
5. Nodes and Junctions in Action
Okay, so we've defined nodes and junctions, explained their relationship, and looked at examples. But why should you care? Here are a few ways this knowledge can be useful:
Problem Solving: When faced with a complex problem, breaking it down into nodes and junctions can help you identify the key areas to focus on. This approach is often used in project management and process optimization.
System Design: Whether you're designing a computer network, a transportation system, or a business process, understanding nodes and junctions is crucial for creating efficient and resilient systems. It helps you anticipate potential bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
Data Analysis: In data analysis, nodes and junctions can be used to represent relationships between different data points. This can help you identify patterns and trends that might otherwise be missed.
Simply Understanding the World Around You: From the flow of traffic to the spread of information on the internet, nodes and junctions are everywhere. Recognizing these concepts can help you make sense of the complex systems that shape our world.So next time you're stuck in traffic, remember the nodes and junctions at play. You might just find yourself appreciating the complexity — or at least, have something to think about while you wait!

Difference Between Loop Mesh Node Element Junction And Branches What
Frequently Asked Questions
6. Your Questions Answered!
Still a little fuzzy on nodes and junctions? Here are some common questions:
Q: Is every intersection a junction?
A: Technically, yes. An intersection is a point where two or more roads cross, fitting the definition of a junction. However, depending on the context, some may differentiate between minor crossings and major intersections.
Q: Can a node be part of multiple junctions?
A: Absolutely! Think of a major city that serves as a hub for several different transportation routes. That city (the node) is part of multiple junctions connecting different regions.
Q: Why is it important to differentiate between nodes and junctions?
A: Differentiating between the two helps in analyzing system complexities. Identifying junctions pinpoints crucial interaction points needing special attention for optimization or potential problem mitigation. Treating every node as equal can obscure these important strategic locations.